终结操作
foreach
对流中的元素进行遍历操作,我们通过传入的参数去指定对遍历到的元素进行什么具体操作。
输出所有作家的名字:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.distinct()
.forEach(name -> System.out.println(name));
}
结果:
蒙多
亚拉索
易
Process finished with exit code 0
count
可以获取当前流中元素的个数
打印作家的所出书籍的数目,注意删除重复元素:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
long count = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.count();
System.out.println(count);
}
结果:
6
Process finished with exit code 0
IDEA调试:

min & max
求流中的最值
分别获取这些作家的所出书籍的最高分和最低分并打印:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Integer> min = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.map(book -> book.getScore())
.min((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
System.out.println(min.orElse(-1));
Optional<Integer> max = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.map(book -> book.getScore())
.max((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
System.out.println(max.orElse(-1));
}
结果:
56
100
Process finished with exit code 0
collect
把当前流转换成一个集合。
获取一个存放所有作者名字的List集合:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
List<String> list = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
}
结果:
[蒙多, 亚拉索, 易, 易]
Process finished with exit code 0
获取一个所有书名的Set集合:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Set<String> set = authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.map(book -> book.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
}
结果:
[那风吹不到的地方, 你的剑就是我的剑, 刀的两侧是光明与黑暗, 风与剑, 吹或不吹, 一个人不能死在同一把刀下]
Process finished with exit code 0
获取一个Map集合,map的key为作者名,value为List<Book>:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Map<String, List<Book>> map = authors.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(author -> author.getName(), author -> author.getBooks()));
System.out.println(map);
}
程序出现异常:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Duplicate key [Book(id=5, name=你的剑就是我的剑, category=爱情, score=56, intro=无法想象一个武者能对他的伴侣这么的宽容), Book(id=6, name=风与剑, category=个人传记, score=100, intro=两个哲学家灵魂和肉体的碰撞会激起怎么样的火花呢?), Book(id=6, name=风与剑, category=个人传记, score=100, intro=两个哲学家灵魂和肉体的碰撞会激起怎么样的火花呢?)]
at java.util.stream.Collectors.lambda$throwingMerger$0(Collectors.java:133)
at java.util.HashMap.merge(HashMap.java:1253)
at java.util.stream.Collectors.lambda$toMap$58(Collectors.java:1320)
at java.util.stream.ReduceOps$3ReducingSink.accept(ReduceOps.java:169)
at java.util.ArrayList$ArrayListSpliterator.forEachRemaining(ArrayList.java:1374)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.copyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:481)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.wrapAndCopyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:471)
at java.util.stream.ReduceOps$ReduceOp.evaluateSequential(ReduceOps.java:708)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.evaluate(AbstractPipeline.java:234)
at java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline.collect(ReferencePipeline.java:499)
at com.sanfen.StreamDemo01.main(StreamDemo01.java:25)
Process finished with exit code 1
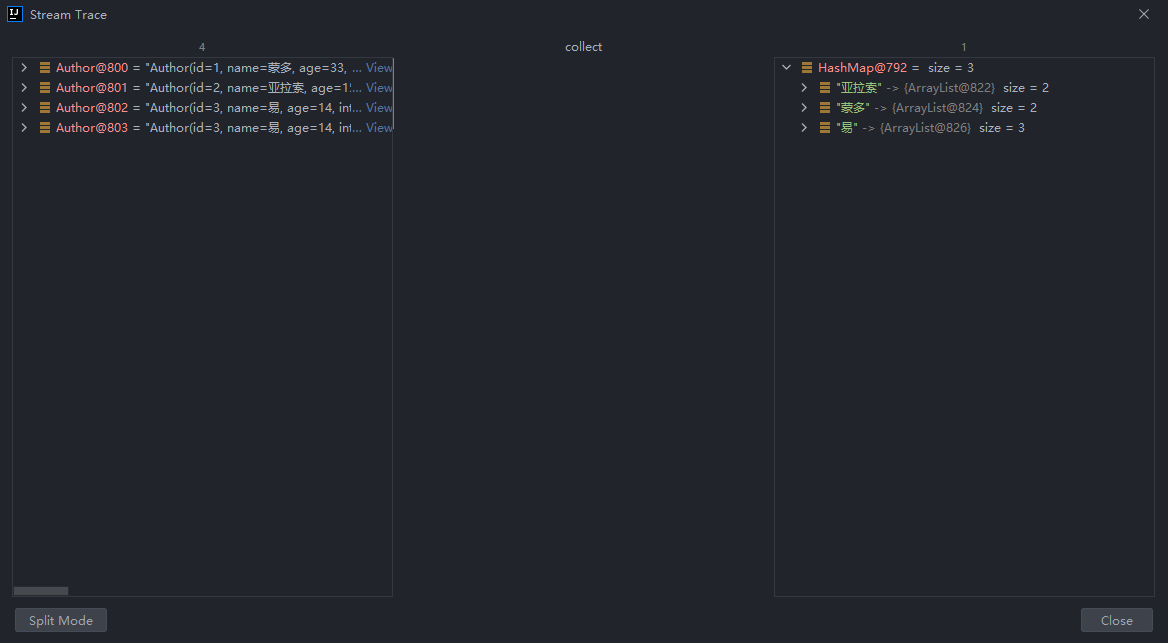
发现是map的key重复了,因为作者名有重复的,我们需要加一个重复判断,任取一个:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Map<String, List<Book>> map = authors.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(author -> author.getName(), author -> author.getBooks(), (books1, books2) -> books1));
System.out.println(map);
}
结果:
{亚拉索=[Book(id=3, name=那风吹不到的地方, category=哲学, score=85, intro=带你用思维去领略世界的尽头), Book(id=4, name=吹或不吹, category=爱情,个人传记, score=56, intro=一个哲学家的恋爱观注定很难把他所在的时代理解)], 蒙多=[Book(id=1, name=刀的两侧是光明与黑暗, category=哲学,爱情, score=88, intro=用一把刀划分了爱恨), Book(id=2, name=一个人不能死在同一把刀下, category=个人成长,爱情, score=99, intro=讲述如何从失败中明悟真理)], 易=[Book(id=5, name=你的剑就是我的剑, category=爱情, score=56, intro=无法想象一个武者能对他的伴侣这么的宽容), Book(id=6, name=风与剑, category=个人传记, score=100, intro=两个哲学家灵魂和肉体的碰撞会激起怎么样的火花呢?), Book(id=6, name=风与剑, category=个人传记, score=100, intro=两个哲学家灵魂和肉体的碰撞会激起怎么样的火花呢?)]}
Process finished with exit code 0
IDEA调试:
查找与匹配
anyMatch
可以用来判断是否有任意符合匹配条件的元素,结果为boolean类型。
判断是否有年龄在29以上的的作家:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean anyMatch = authors.stream()
.anyMatch(author -> author.getAge() > 29);
System.out.println(anyMatch);
}
结果:
true
Process finished with exit code 0
IDEA调试:
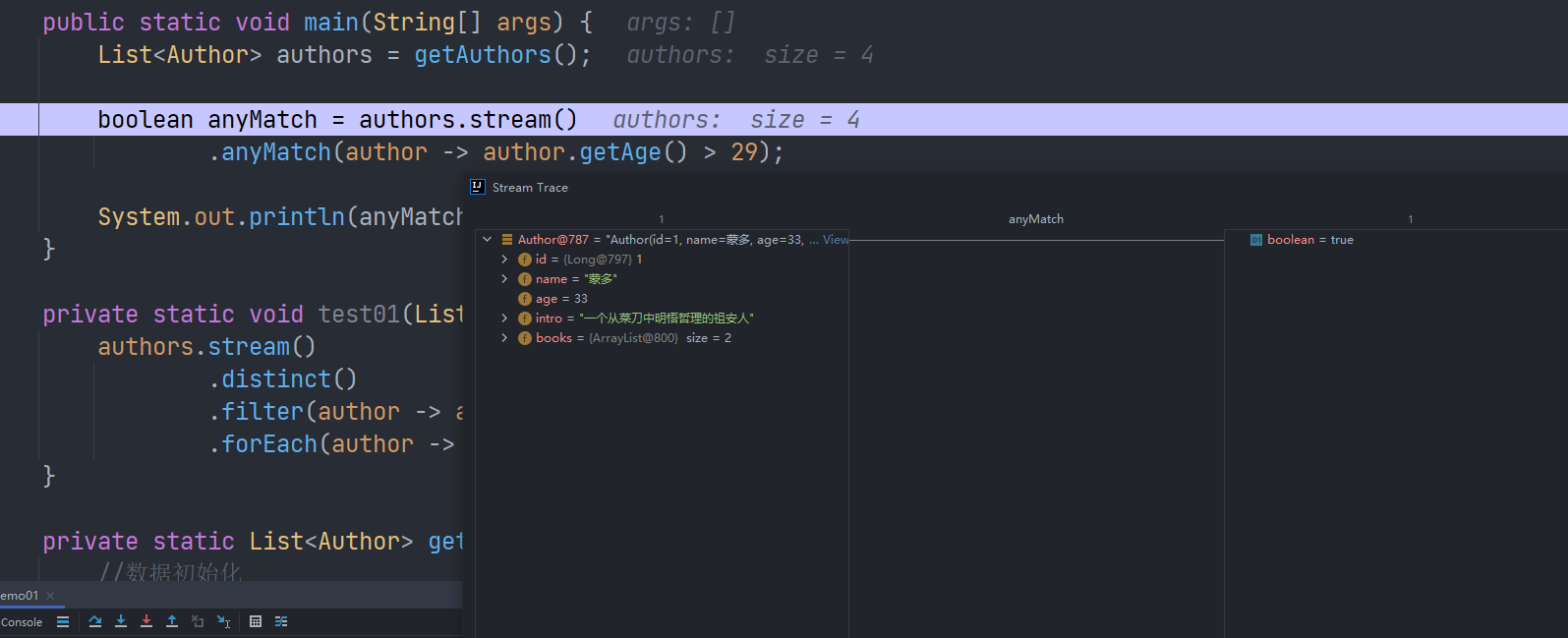
allMatch
可以用来判断是否都符合匹配条件,结果为boolean类型。如果都符合结果为true,否则为false。
判断是否所有的作家都是成年人:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean anyMatch = authors.stream()
.allMatch(author -> author.getAge() >= 18);
System.out.println(anyMatch);
}
false
Process finished with exit code 0
IDEA调试:
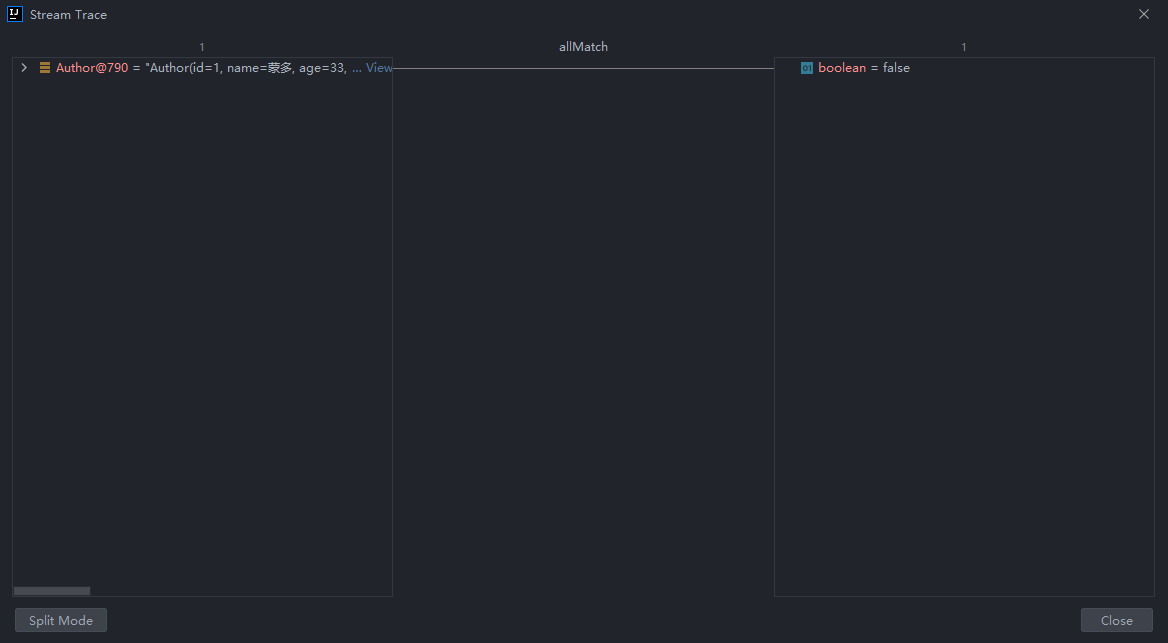
noneMatch
可以判断流中的元素是否都不符合条件。如果都不符合结果为true,否则结果为false。
判断作家是否都没有超过100岁:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean anyMatch = authors.stream()
.noneMatch(author -> author.getAge() > 100);
System.out.println(anyMatch);
}
结果:
true
Process finished with exit code 0
findAny
获取流中的任意一个元素。该方法没有办法保证获取的一定是流中的第一个元素。
获取任意一个大于18的作家,如果存在就输出名字:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Author> optional = authors.stream()
.filter(author -> author.getAge() > 18)
.findAny();
optional.ifPresent(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
findFirst
获取流中的第一个元素。
获取一个年龄最小的作家,并输出名字:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Author> first = authors.stream()
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge())
.findFirst();
first.ifPresent(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
reduce
对流中的数据按照你制定的计算方式计算出一个结果。reduce的计算方式就是把stream中的元素组合起来,我们可以传入一个初始值。它会按照我们的计算方式依次拿流中的元素和在初始化值的基础上进行计算,计算结果再和后面的元素计算。
reduce两个参数的内部计算方式:
T result = identity;
for (T element : this stream)
result = accumulator.apply(result, element)
return result;
使用reduce求所有作者年龄的和:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer res = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(0, (result, element) -> result + element);
System.out.println(res );
}
IDEA调试:
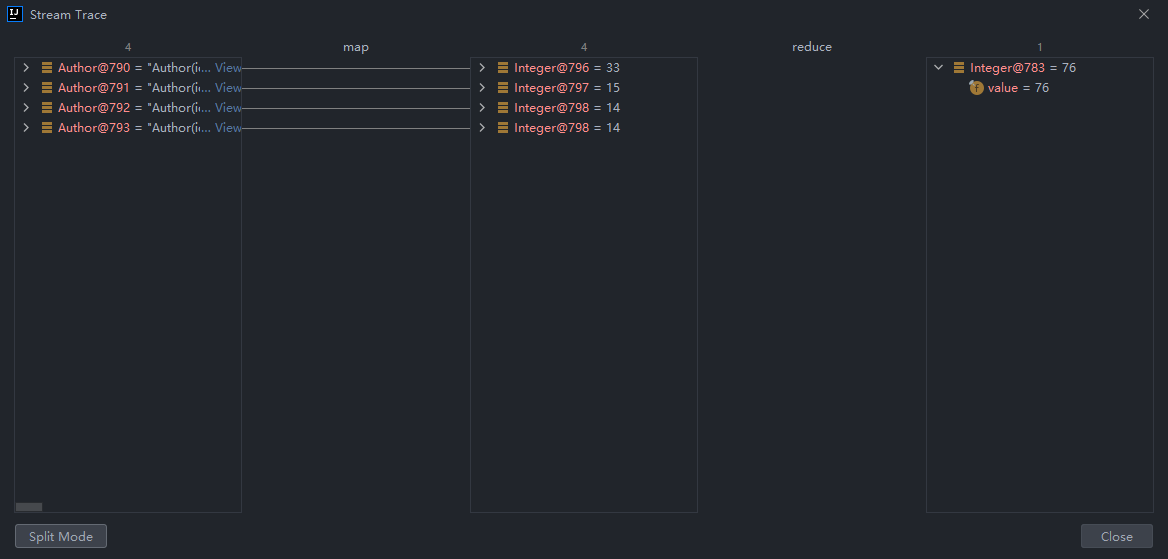
使用reduce求所有作者中年龄的最大值:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer res = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(Integer.MIN_VALUE, (result, element) -> element > result ? element : result);
System.out.println(res );
}
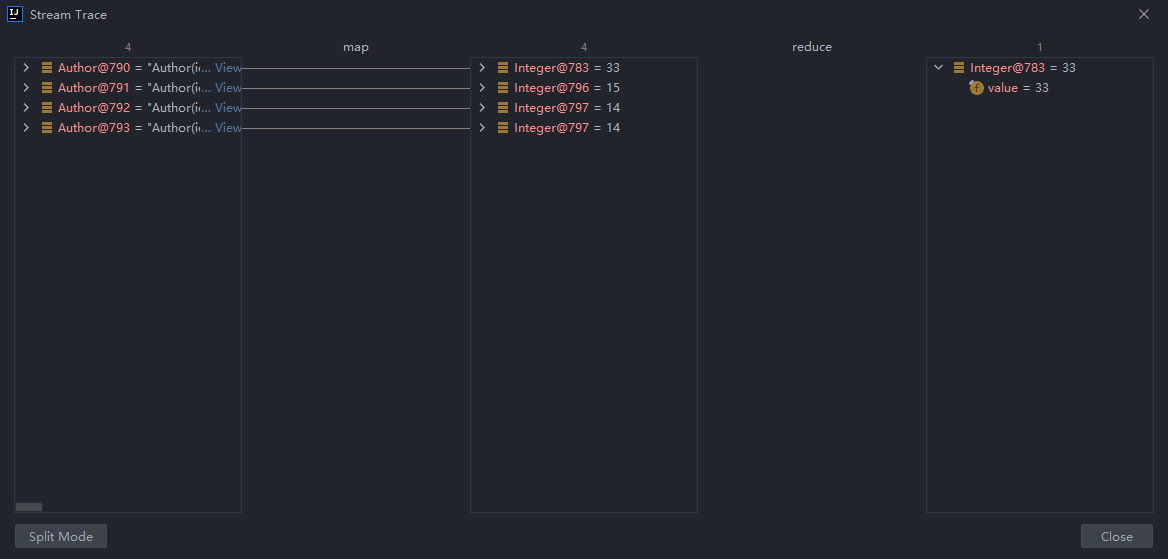
使用reduce求所有作者中年龄的最小值:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer res = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(Integer.MAX_VALUE, (result, element) -> element < result ? element : result);
System.out.println(res );
}
IDEA调试:
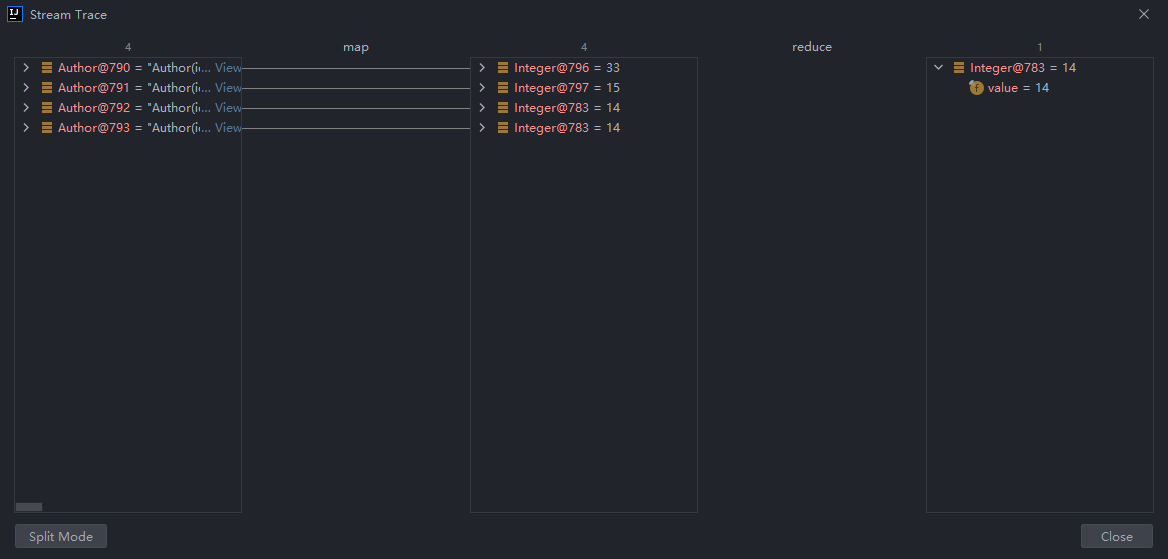
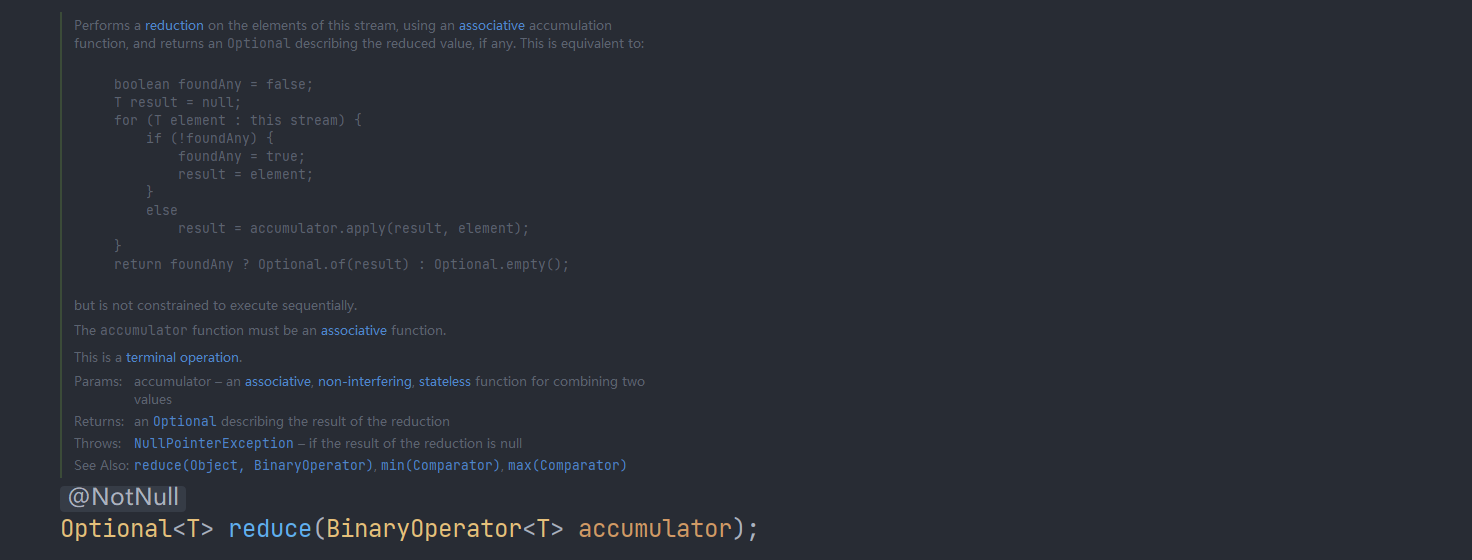
reduce一个参数的重载形式:会把流中的第一个元素作为初始化值。
boolean foundAny = false;
T result = null;
for (T element : this stream) {
if (!foundAny) {
foundAny = true;
result = element;
}
else
result = accumulator.apply(result, element);
}
return foundAny ? Optional.of(result) : Optional.empty();
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Integer> min = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce((result, element) -> element < result ? element : result);
min.ifPresent(age -> System.out.println(age));
}