线程的创建 - 实现Runnable接口
大约 2 分钟Java多线程详解
- 实现Runnable接口。
- 重写run()方法。
- 创建线程对象,执行线程需要丢入Runnable接口实现类。调用start()方法启动线程。
public class TestThread3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在看代码===>" + i);
}
}
// main线程,主线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建Runnable接口实现类对象
TestThread3 testThread3 = new TestThread3();
// 创建线程对象,通过线程对象来开启我们的线程,代理
new Thread(testThread3).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习多线程==>" + i);
}
}
}
结果:
我在学习多线程==>0
我在学习多线程==>1
我在学习多线程==>2
我在学习多线程==>3
我在学习多线程==>4
我在学习多线程==>5
我在学习多线程==>6
我在学习多线程==>7
我在学习多线程==>8
我在学习多线程==>9
我在学习多线程==>10
我在看代码===>0
我在看代码===>1
我在看代码===>2
我在看代码===>3
我在看代码===>4
我在看代码===>5
我在看代码===>6
我在看代码===>7
我在看代码===>8
我在看代码===>9
我在看代码===>10
我在看代码===>11
我在看代码===>12
我在看代码===>13
我在看代码===>14
我在看代码===>15
我在学习多线程==>11
我在学习多线程==>12
我在学习多线程==>13
我在学习多线程==>14
我在学习多线程==>15
我在学习多线程==>16
我在学习多线程==>17
我在看代码===>16
我在看代码===>17
我在看代码===>18
我在看代码===>19
我在学习多线程==>18
我在学习多线程==>19
Process finished with exit code 0
Thread类
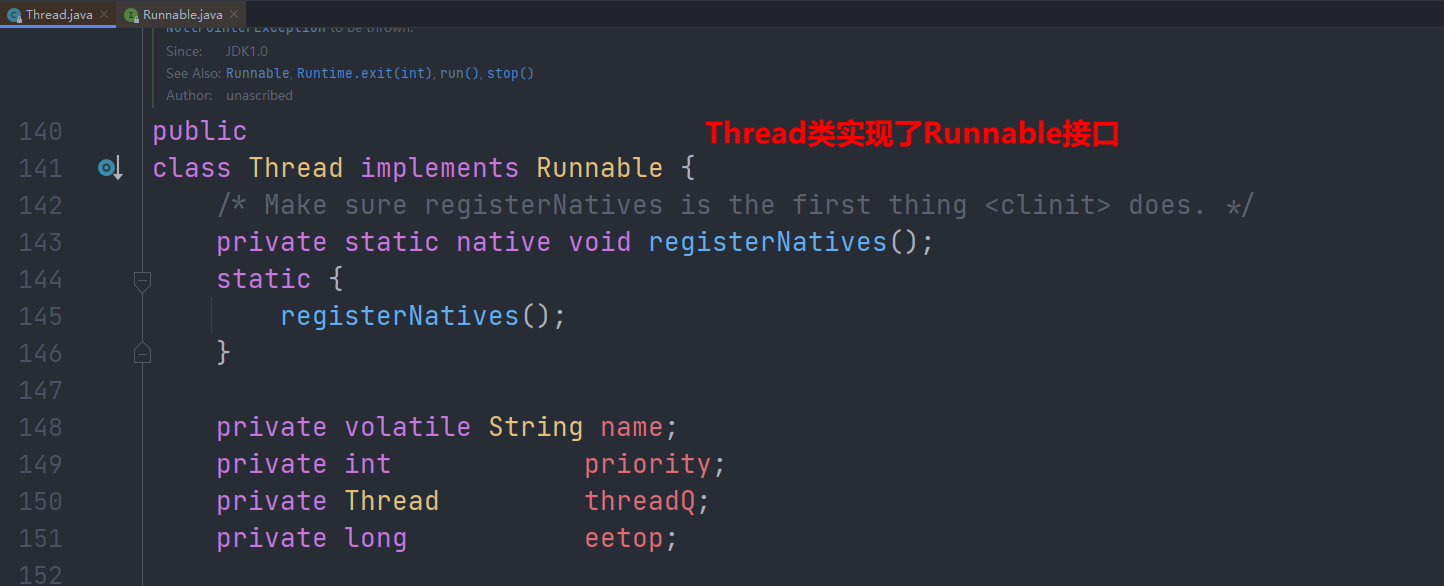
Runnable接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}